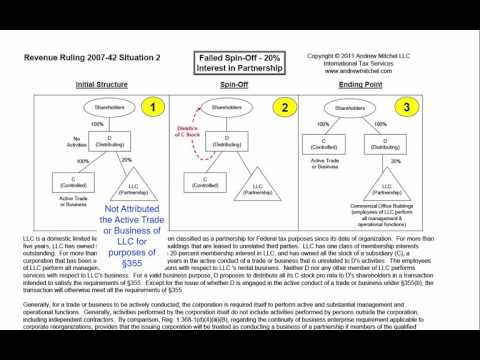
In Revenue Ruling 2007-42, the situation was that the distributing corporation did not have its own active trader business. 2. However, the distributing corporation owned a hundred percent of a controlled corporation that did have an active trader business. 3. Additionally, the distributing corporation owned a twenty percent interest in an LLC that was taxed as a partnership. 4. The partnership was engaged in an active trader business. 5. However, due to the fact that the distributing corporation owned less than one-third of the LLC, it was not attributed the active trader business of the LLC for section 355 purposes. 6. Consequently, when the distributing corporation distributed the shares of control to its shareholders, the transaction did not qualify as a spin-off under code section 355.
Award-winning PDF software





Rev. rul. 2020-18 Form: What You Should Know
Interest on underpayments of tax is set to the rate set in Revenue Procedure 2011-38. Interest on underpayments of tax is not set in Revenue Procedure 2011-38. Interest on federal income tax underpayments and federal income tax overpayments, including federal income taxes underpayments and underpayments, and interest on federal income tax overpayments, is calculated in accordance with the formulas set in Revenue Procedure 2011-38 on a quarterly basis. Tax Notes from the IRS (Treas. Reg. Sec. 1.666-2(d) and Revenue Procedure 2011-38) provide the interest rate on the underpayments of tax and the corresponding percentage rate on the overpayments of tax, including an annual adjustment in Rev. Run. 2009-14 for any federal income tax underpayment of tax or federal income tax overpayment. Interest is the difference between the amount received before the tax was underpaid and the amount received after the tax was paid (and does not include any amounts from prior tax years). It is measured in percentage points. The annual percentage rate is multiplied by 100 percent. The annual interest rate is set to the lowest of the following rates: On an underpayment of tax, the interest is 2.5 percent. On an overpayment of tax, the interest is 2.5 percent. For tax underpayments and overpayments that are not covered. This term is used to describe underpayments of tax if the total tax due for the year is more than what was paid, but not more than the tax rate for the year. For example, say a tax return for 2025 is filed, and 1,000 is paid in taxes. There is an overpayment of tax of 300. The following year, tax is paid, and 1,000 is received as a penalty, which is not part of the tax underpayment. In such a case, the annual interest rate is not the base case rate, and it is calculated from the base case rate. The base case rate is 2 percent. The total tax underpayment is 300 multiplied by the 2.5 percent annual underpayment penalty rate. Interest is calculated as 1 percent of the 300 overpayment after all penalties and interest have been paid, or 0.5 percent of the overpayment. Example: In 2015, a tax return for 2025 is filed. A penalty of 300 is assessed.
online solutions help you to manage your record administration along with raise the efficiency of the workflows. Stick to the fast guide to do Form 8869, steer clear of blunders along with furnish it in a timely manner:
How to complete any Form 8869 Online: - On the site with all the document, click on Begin immediately along with complete for the editor.
- Use your indications to submit established track record areas.
- Add your own info and speak to data.
- Make sure that you enter correct details and numbers throughout suitable areas.
- Very carefully confirm the content of the form as well as grammar along with punctuational.
- Navigate to Support area when you have questions or perhaps handle our assistance team.
- Place an electronic digital unique in your Form 8869 by using Sign Device.
- After the form is fully gone, media Completed.
- Deliver the particular prepared document by way of electronic mail or facsimile, art print it out or perhaps reduce the gadget.
PDF editor permits you to help make changes to your Form 8869 from the internet connected gadget, personalize it based on your requirements, indicator this in electronic format and also disperse differently.
Video instructions and help with filling out and completing Rev. rul. 2020-18